|
Patch Low Rank MRI
|
Patch based low rank regularization for Dynamic MRIHuisu Yoon, Kyung Sang Kim, Daniel Kim, Yoram Bresler, and J.C. Ye "Motion Adaptive Patch-Based Low-Rank Approach for Compressed Sensing Cardiac Cine MRI", IEEE Trans. Medical Imaging, , Vol. 33, No. 11, pp.2069-2085, Nov. 2014.
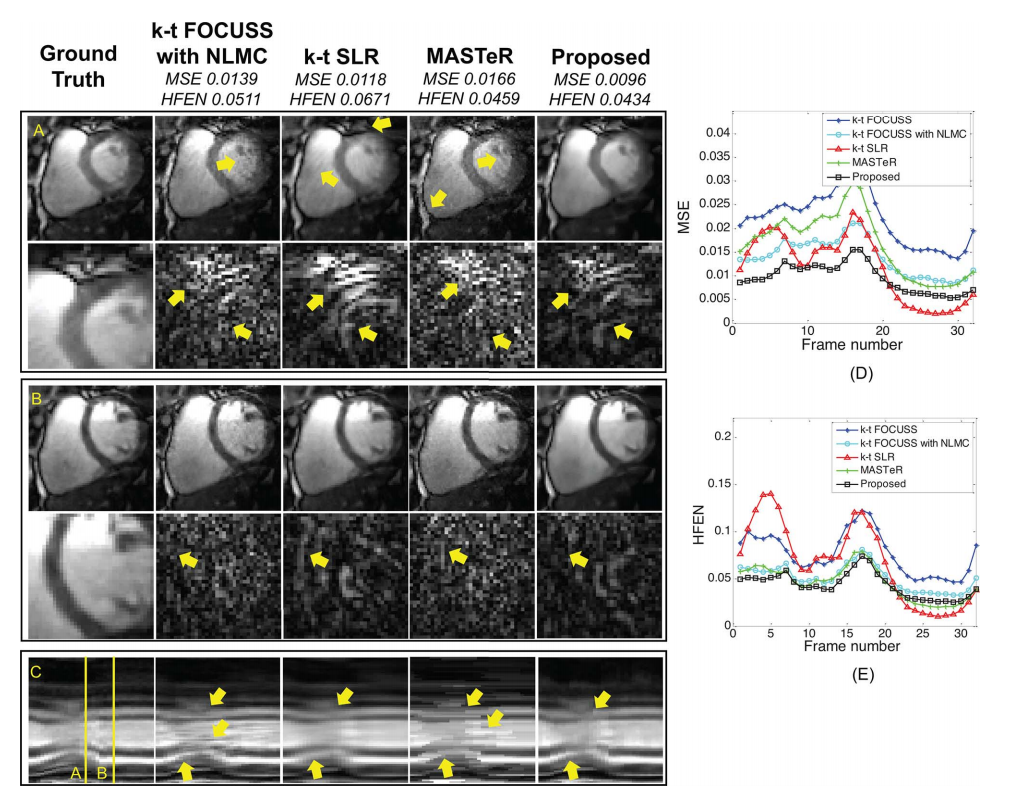
One of the technical challenges in cine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is to reduce the acquisition time to enable the high spatio-temporal resolution imaging of a cardiac volume within a short scan time. Recently, compressed sensing approaches have been investigated extensively for highly accelerated cine MRI by exploiting transform domain sparsity using linear transforms such as wavelets, and Fourier. However, in cardiac cine imaging, the cardiac volume changes significantly between frames, and there often exist abrupt pixel value changes along time. In order to effectively sparsify such temporal variations, it is necessary to exploit temporal redundancy along motion trajectories. This paper introduces a novel patch-based reconstruction method to exploit geometric similarities in the spatio-temporal domain. In particular, we use a low rank constraint for similar patches along motion, based on the observation that rank structures are relatively less sensitive to global intensity changes, but make it easier to capture moving edges. A Nash equilibrium formulation with relaxation is employed to guarantee convergence. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm clearly reconstructs important anatomical structures in cardiac cine image and provides improved image quality compared to existing state-of-the-art methods such as k-t FOCUSS, k-t SLR, and MASTeR.
Software Requirements MATLAB (Mathworks, Natick, MA, http://www.mathworks.com).
|
|
ABOUT US
Our research activities are primarily focused on the signal processing and machine learning for high-resolution high-sensitivity image reconstruction from real world bio-medical imaging systems. Such problems pose interesting challenges that often lead to investigations of fundamental problems in various branches of physics, mathematics, signal processing, biology, and medicine. While most of the biomedical imaging researchers are interested in addressing this problem using off-the-self tools from signal processing, machine learning, statistics, and optimization and combining their domain-specific knowledge, our approaches are unique in the sense that I believe that actual bio-medical imaging applications are a source of endless inspiration for new mathematical theories and we are eager to solve both specific applications and application-inspired fundamental theoretical problems.
|
CONTACT US
Bio Imaging. Signal Processing & Learning
Graduate School of AI KAIST 291 Daehak-ro, Yuseong-gu Daejeon 305-701, Korea Copyright (c) 2014, BISPL All Rights Reserved. |
|